
The impact of artificial intelligence on software development is clearly visible. It is transforming the field by increasing speed and efficiency for developers. Digital transformation enables organizations to use production assets, infrastructure, and machinery in a smarter and more efficient way. The combination of Azure IoT and Artificial Intelligence (AI) makes it possible not only to monitor processes, but also to analyze them predictively and optimize them autonomously. For example, a factory can detect failures before they occur, reducing downtime and allowing maintenance to be scheduled more efficiently. A production line can also continuously adjust itself based on real-time data, ensuring ongoing improvements in performance and quality.
These applications are not a vision of the future, but can already be realized today with Azure IoT. In this article, we will explore how this technology can help organizations improve reliability, efficiency, and decision-making.
From vision to action
Across manufacturing plants, warehouses, energy grids, and other smart infrastructure, Azure IoT and its complementary tools support the transition from traditional operations to intelligent systems that are more efficient, secure, and data-driven. From the smallest sensor to industrial-grade servers, Azure IoT today enables device connectivity, real-time data collection, AI execution at the edge, and seamless integration with cloud-based analytics.
The outcome is tangible: reduced downtime, faster decision-making, and predictive insights that provide a significant competitive advantage.
With Azure IoT, organizations are not simply adopting new technology; they are embedding business intelligence directly at the operational edge, where it has the greatest impact.
Azure IoT
Azure IoT is Microsoft’s cloud platform designed for connecting, managing, and monitoring physical devices such as machines and sensors over the internet.
The platform consists of two main services:
- Azure IoT Hub: the central cloud gateway that enables secure, two-way communication between devices and the cloud.
- Azure IoT Central: a ready-to-use SaaS platform that allows organizations to quickly visualize and manage devices without the need for coding.
Key applications of Azure IoT include:
- Transmitting all collected data to the cloud for analysis and storage.
- Collecting real-time data from machines.
- Controlling devices remotely.
- Monitoring device health and performance.
Azure IoT Edge
Azure IoT Edge is the edge computing extension of Azure IoT. It enables “cloud intelligence” to run directly on devices, even when they are offline.
With IoT Edge, organizations can deploy:
- AI and machine learning (ML) models
- Stream Analytics jobs
- Custom business logic within containers
- Azure services such as Functions or SQL directly on the device
IoT Edge is compatible with a wide range of hardware, including industrial PCs, Azure Stack Edge, and Raspberry Pi. The platform is built around three core components:
- IoT Edge Hub: a local equivalent of Azure IoT Hub, responsible for routing data and managing connectivity
- IoT Edge Runtime: software that manages modules and device communication
- IoT Edge Modules: containerized applications (similar to Docker) that execute logic or ML models
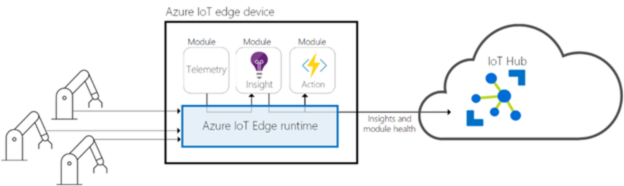
How they work together
To illustrate how Azure IoT and Azure IoT Edge complement one another, consider the following analogy: Azure IoT functions as a company’s headquarters, where strategy and coordination take place. Azure IoT Edge, in this context, represents a branch office, where real-time operations occur and decisions can be made locally without always consulting the headquarters.
The process works as follows:
- Azure IoT Hub (cloud) securely connects all devices, whether they are sensors, edge gateways, or other hardware.
- IoT Edge devices connect to IoT Hub in the same way as regular devices, but with added intelligence and local processing capabilities.
- Workloads such as ML models or analytics jobs are deployed from the cloud to the edge via IoT Hub.
- The edge device executes these workloads locally, enabling real-time data processing.
- Only the relevant insights are sent back to Azure.
- Within Azure, the data can then be stored, analyzed, or visualized using services such as Power BI, Azure Digital Twins, or Azure Machine Learning.
Extra tooling
While Azure IoT provides a strong foundation for device connectivity and management, practical IoT solutions often require more than basic communication between devices. To enable smarter, safer, and more sophisticated applications, Azure includes additional tools that extend the platform’s functionality.
Two key components in this regard are Azure Digital Twins and Azure Sphere. These technologies add important layers of intelligence and security to an IoT ecosystem: Digital Twins support advanced insights through virtual modeling, while Sphere ensures end-to-end device protection.
Azure Digital Twins
Azure Digital Twins is a platform-as-a-service (PaaS) offering from Microsoft that enables the creation of digital replicas of real-world environments such as buildings, factories, utilities, or even entire cities. These digital models support real-time simulation, monitoring, and optimization of physical spaces by integrating with IoT devices and other data sources.

Azure Digital Twins provides a range of features that allow organizations to model, monitor, and optimize physical environments:
- Modeling the physical world: Digital twins can be defined using the Digital Twins Definition Language (DTDL). This makes it possible to model physical entities (e.g., rooms, elevators, machines), their properties (e.g., temperature, status), and their relationships (e.g., “Room A is in Building X”).
- Live data integration: IoT devices and other data sources can be connected to feed real-time telemetry into digital models.
- Contextual insights: The platform enables an understanding of how elements relate to one another spatially, logically, or hierarchically.
- Simulation and prediction: Organizations can run simulations or apply analytics and AI to optimize performance, detect anomalies, or predict future states.
- Event-driven architecture: Systems can respond automatically to changes through event routing and integration with services such as Azure Functions or Event Grid.
Real-world applications of Azure Digital Twins include:
- Digitally representing and managing complex physical environments
- Enabling real-time monitoring and automated responses
- Running simulations or “what-if” analyses
- Supporting predictive maintenance, occupancy tracking, and energy optimization
Azure Sphere
In an increasingly connected environment, IoT devices are frequent targets for cyberattacks. Azure Sphere addresses this challenge by providing a comprehensive security platform specifically designed for Internet-connected microcontroller (MCU) devices.
Developed by Microsoft, Azure Sphere delivers end-to-end protection from the silicon hardware to the cloud. It ensures that even the smallest IoT devices, such as sensors, controllers, smart meters, or household appliances, are secure by design and remain protected throughout their lifecycle.

Azure Sphere is built around three main elements that work together to provide comprehensive device security:
- Azure Sphere-certified MCU (Microcontroller Unit) – a purpose-built chip that includes:
- A secure processing environment embedded in the hardware
- A security subsystem for cryptographic operations and secure boot
- Support for running real-time and application-level code on separate cores
- Azure Sphere OS – a custom Linux-based operating system that:
- Provides container-like isolation between components
- Includes multiple defense-in-depth mechanisms
- Ensures secure execution of applications and communication
- Azure Sphere Security Service (cloud) – a cloud-based service that:
- Continuously monitors device health
- Delivers over-the-air (OTA) updates
- Authenticates devices and detects potential security threats
Together, these components ensure that IoT devices are protected by design and maintain security throughout their lifecycle.

Bringing intelligence to the edge
The full potential of Azure IoT emerges when AI and machine learning (ML) are deployed directly on edge devices. This approach enables real-time decision-making, even without continuous cloud connectivity.
Why AI at the Edge?
In traditional IoT architectures, devices typically collect data and transmit it to the cloud for analysis. However, in industries where even milliseconds matter such as energy, healthcare, or manufacturing, this delay can be critical. Azure IoT Edge allows AI models to run locally on devices, enabling systems to analyze, respond, and adapt immediately as data is collected.
Workflow for AI/ML on Azure IoT Edge
- Train the model in the cloud: Use Azure Machine Learning or other frameworks to train a model with historical or labeled data.
- Export the model to a container: Convert the trained model to a compatible format (ONNX, TensorFlow, PyTorch, etc.) and package it in a Docker container for deployment on IoT Edge.
- Deploy via Azure IoT Hub: Use IoT Hub to deploy the containerized model to IoT Edge devices, integrating the model as an IoT Edge module.
- Run inference at the edge: Devices process real-time sensor data locally to make predictions, detect issues, or classify events, without sending raw data to the cloud. Only actionable results are transmitted.
- Send insights to the cloud: Transmit optimized summaries, alerts, or aggregated statistics to Azure for further analysis or storage.
Real-World Examples
- Agriculture: Edge devices process soil and climate data to determine local irrigation schedules using predictive models.
- Factories: Edge devices analyze vibration data from motors to predict mechanical failures before they occur.
- Logistics: Cameras run ML models to recognize license plates or detect shipment tampering.
- Healthcare: Wearables with Azure Sphere MCUs detect anomalies in patient vitals and trigger immediate alerts without cloud delays.
Bottom line
The Azure IoT ecosystem achieves its full potential when combined with IoT Edge and integrated AI and machine learning capabilities.
In this architecture, Azure IoT functions as the central nervous system, managing and monitoring devices from the cloud. Azure IoT Edge acts as the local intelligence, enabling devices to operate autonomously and make decisions close to where data is generated, without relying on constant cloud connectivity.
This approach extends beyond traditional IoT, delivering what is commonly referred to as the Intelligent Edge, powered by Azure.